Best News | This years Best News Treats and Viral Events
Understanding Klebsiella Oxytoca: A Guide To Its Pathogenesis, Epidemiology, And Prevention
Are you looking for a comprehensive guide to Klebsiella oxytoca, a bacterium that can cause a variety of infections? Understanding Klebsiella Oxytoca: A Guide To Its Pathogenesis, Epidemiology, And Prevention has just been published by [Publisher Name].
Editor's notes: Understanding Klebsiella Oxytoca: A Guide To Its Pathogenesis, Epidemiology, And Prevention is an important resource for healthcare professionals, researchers, and anyone else who wants to learn more about this pathogen.
We've done the work of analyzing and distilling the information on Klebsiella oxytoca into this easy-to-understand guide. We've covered everything from its pathogenesis to its epidemiology and prevention. So whether you're a doctor or a patient, this guide has something for you.
Key differences between Klebsiella oxytoca and other Klebsiella species
| Characteristic | Klebsiella oxytoca | Other Klebsiella species |
|---|---|---|
| Pathogenicity | Less pathogenic than other Klebsiella species | More pathogenic than Klebsiella oxytoca |
| Epidemiology | Found in the environment and the human gastrointestinal tract | Found in the human respiratory tract |
| Prevention | Can be prevented by good hygiene practices | Can be prevented by vaccination |
Pathogenesis of Klebsiella oxytoca
Klebsiella oxytoca is a Gram-negative bacterium that can cause a variety of infections, including pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and bloodstream infections. The bacterium produces a number of virulence factors that help it to cause disease, including fimbriae, adhesions, and capsules.
Epidemiology of Klebsiella oxytoca
Klebsiella oxytoca is a common bacterium that is found in the environment and the human gastrointestinal tract. The bacterium is spread through contact with contaminated food or water, or through contact with an infected person.
Prevention of Klebsiella oxytoca
Klebsiella oxytoca infections can be prevented by practicing good hygiene, including washing your hands frequently, avoiding contact with contaminated food or water, and getting vaccinated.
FAQ
This section presents a series of frequently asked questions (FAQs) to provide a more in-depth understanding of Understanding Klebsiella Oxytoca: A Guide To Its Pathogenesis, Epidemiology, And Prevention.

Microorganisms | Free Full-Text | Understanding the Interactions - Source www.mdpi.com
Question 1: What are the most common clinical presentations of Klebsiella oxytoca infections?
Answer: Klebsiella oxytoca can cause various infections, including pneumonia, urinary tract infections, bloodstream infections, and meningitis. It is important to note that the specific clinical presentation can vary depending on the site of infection.
Question 2: How is Klebsiella oxytoca transmitted?
Answer: Klebsiella oxytoca is primarily transmitted through contact with contaminated surfaces or objects, as well as through the inhalation of airborne droplets produced by infected individuals.
Question 3: Who is at risk of developing Klebsiella oxytoca infections?
Answer: Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with chronic diseases, diabetes, or undergoing immunosuppressive therapy, are at an increased risk of developing Klebsiella oxytoca infections. Additionally, those who have recently undergone surgery or have invasive medical devices are also at higher risk.
Question 4: How is Klebsiella oxytoca diagnosed?
Answer: Klebsiella oxytoca is typically diagnosed through laboratory testing of clinical specimens, such as blood, urine, or respiratory secretions. Specific tests may include blood cultures, urine analysis, or molecular assays.
Question 5: What are the treatment options for Klebsiella oxytoca infections?
Answer: Treatment for Klebsiella oxytoca infections typically involves the administration of antibiotics. The specific choice of antibiotic will depend on the site and severity of the infection, as well as the susceptibility of the strain to different antibiotics.
Question 6: What are the preventive measures for Klebsiella oxytoca infections?
Answer: Preventive measures include practicing good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing, disinfection of surfaces, and proper handling of food. Additionally, individuals with weakened immune systems should take precautions to avoid contact with potential sources of infection.
By understanding these key aspects of Klebsiella oxytoca, healthcare professionals and individuals can better manage and prevent infections caused by this bacterium.
For further information and a more comprehensive discussion, please refer to the main article on Understanding Klebsiella Oxytoca: A Guide To Its Pathogenesis, Epidemiology, And Prevention.
Tips for Understanding Klebsiella Oxytoca
Klebsiella oxytoca is a Gram-negative bacterium that belongs to the Enterobacteriaceae family. It is an opportunistic pathogen that can cause infections in the respiratory, urinary, gastrointestinal, and bloodstream. The increasing prevalence of K. oxytoca infections, coupled with its ability to develop antibiotic resistance, highlights the importance of understanding its pathogenesis, epidemiology, and prevention strategies. The following tips will provide a comprehensive guide to enhance your understanding of K. oxytoca.
Tip 1:
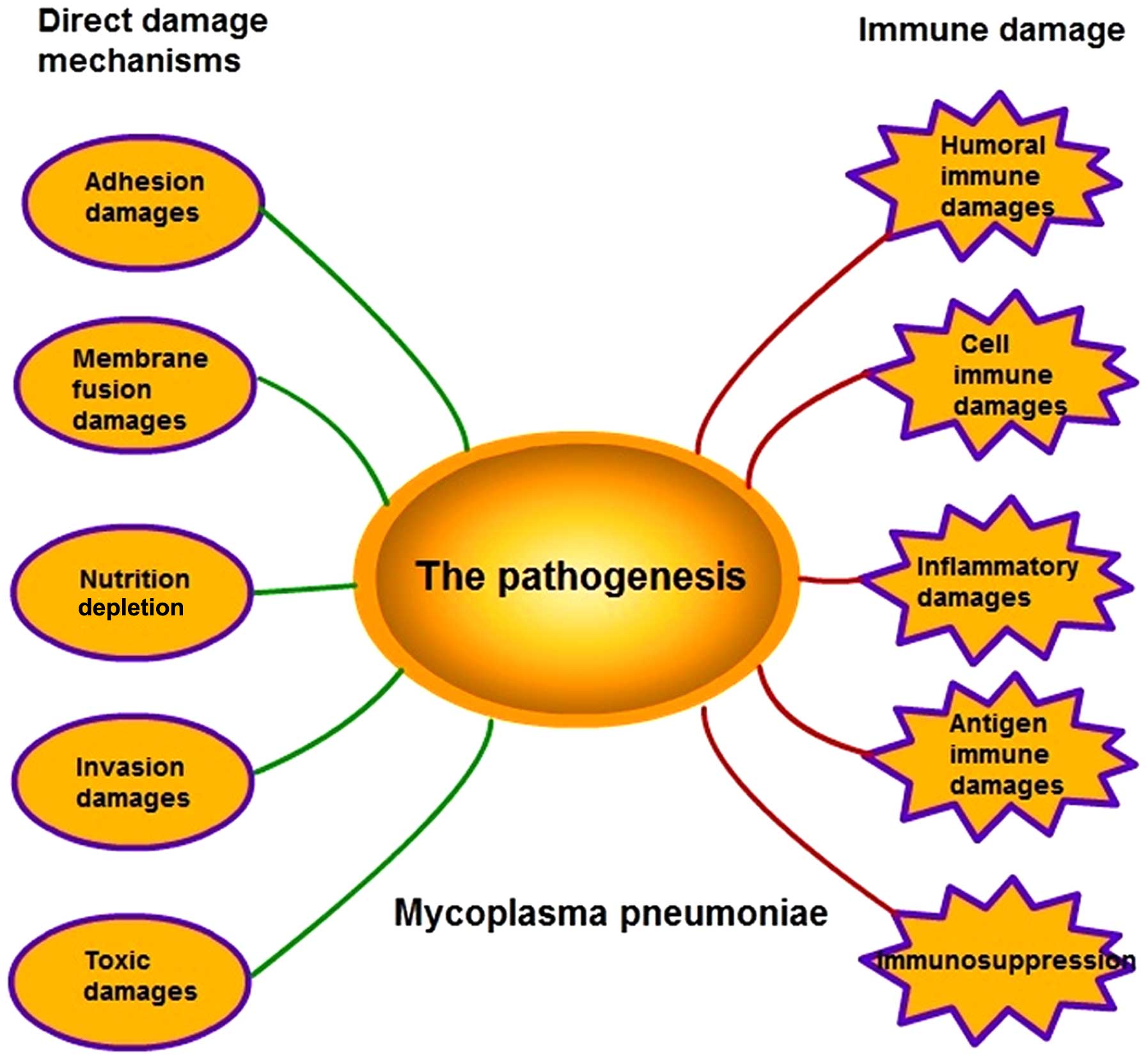
Insights into the pathogenesis of Mycoplasma pneumoniae (Review - Source www.spandidos-publications.com
Recognize the Pathogenesis of K. Oxytoca
Gain a thorough understanding of the mechanisms by which K. oxytoca causes infections. Study its virulence factors, adhesion molecules, and biofilm formation capabilities. This knowledge will aid in developing effective strategies to combat its pathogenicity.
Tip 2:
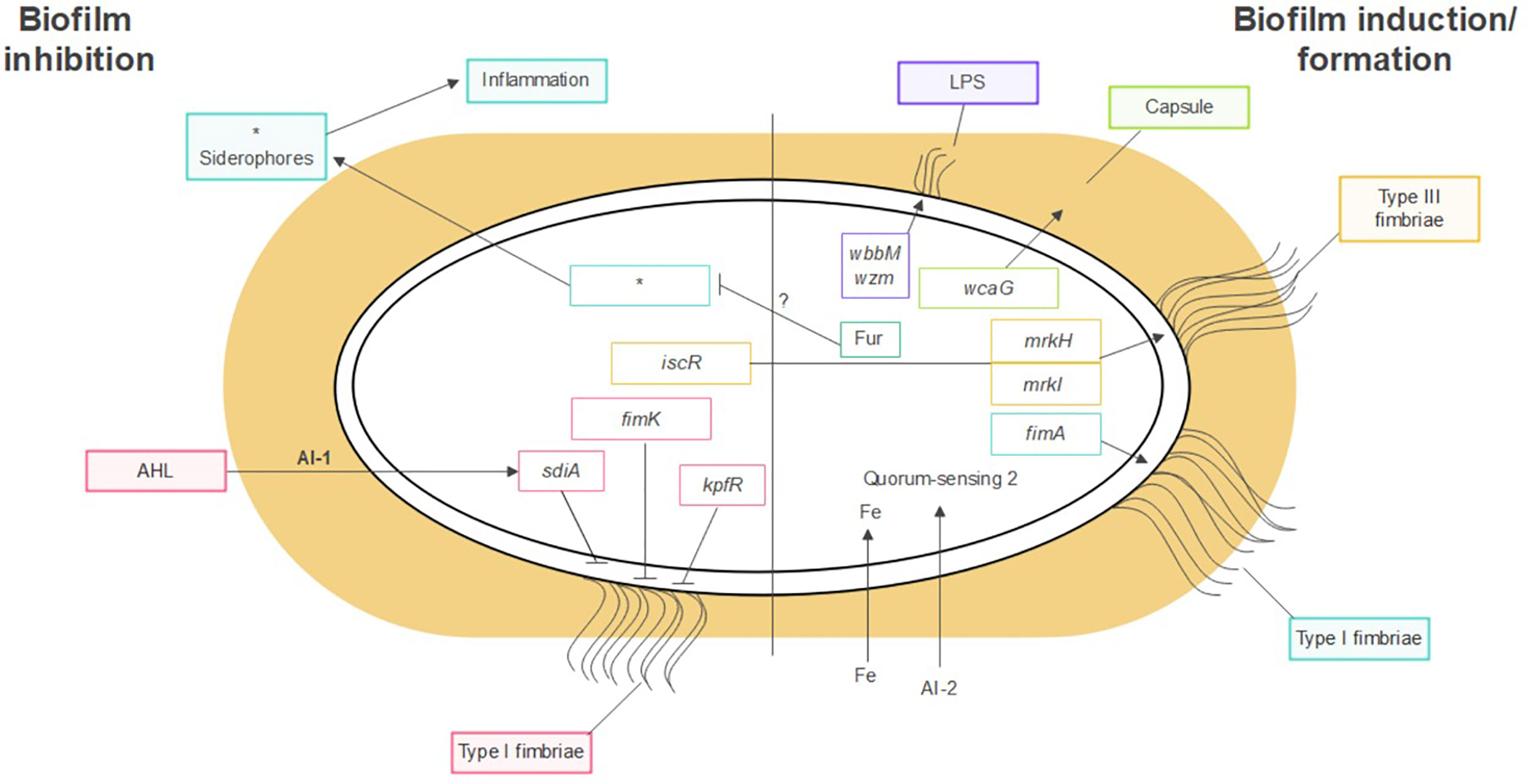
Frontiers | Klebsiella pneumoniae Biofilms and Their Role in Disease - Source www.frontiersin.org
Understand the Epidemiology of K. Oxytoca
Analyze the distribution and prevalence of K. oxytoca infections. Determine the risk factors and populations most susceptible to infection. Understanding the epidemiology will help identify high-risk individuals and guide targeted prevention efforts.
Tip 3:

Klebsiella species: Taxonomy, hypervirulence and multidrug resistance - Source www.thelancet.com
Implement Effective Prevention Measures
Establish comprehensive infection control protocols to reduce the transmission of K. oxytoca. Implement hand hygiene practices, sterilization techniques, and appropriate isolation measures. These preventive strategies are crucial in limiting the spread of infections.
Tip 4:

Epidemiology of Klebsiella oxytoca-Associated Diarrhea Detected by - Source journals.asm.org
Stay Updated on Antibiotic Resistance Patterns
Monitor the emergence and spread of antibiotic resistance among K. oxytoca strains. Conduct regular susceptibility testing to guide appropriate antibiotic selection and minimize the risk of treatment failure. Continuous surveillance is vital for combating antibiotic resistance.
Tip 5:
Microorganisms | Free Full-Text | Characterization of Feruloyl Esterase - Source www.mdpi.com
Promote Research and Collaboration
Support ongoing research to further understand the molecular mechanisms and epidemiology of K. oxytoca infections. Collaborate with experts to develop innovative diagnostic, therapeutic, and preventive strategies. By advancing scientific knowledge, we can effectively address the challenges posed by K. oxytoca.
Summary: Understanding Klebsiella oxytoca is essential for controlling infections, preventing its spread, and developing effective treatment strategies. By implementing these tips, healthcare professionals, researchers, and individuals can contribute to the comprehensive management and understanding of this opportunistic pathogen.
Understanding Klebsiella Oxytoca: A Guide To Its Pathogenesis, Epidemiology, And Prevention
Klebsiella oxytoca, a Gram-negative bacterium, poses significant threats to human health. Understanding its pathogenesis, epidemiology, and prevention is crucial for effective management. Key aspects to consider include:
- Pathogenesis: Colonization and invasion
- Epidemiology: Community and healthcare settings
- Transmission: Contact with contaminated surfaces/fluids
- Prevention: Hand hygiene, environmental disinfection
- Treatment: Antibiotic therapy
- Risk Factors: Compromised immunity, chronic diseases
How to Treat Klebsiella Pneumoniae Bacteria Infections? - Source androclue.com
These aspects are interconnected; colonization precedes infection, while transmission depends on environmental factors. Healthcare settings, with immunocompromised patients, pose higher risks. Prevention measures, such as hand hygiene and surface disinfection, are vital in curbing transmission. Understanding these aspects enables informed decision-making for effective management of Klebsiella oxytoca infections.

Klebsiella oxytoca - USEFUL LECTURE NOTES - Klebsiella oxytoca - Source www.studocu.com
Understanding Klebsiella Oxytoca: A Guide To Its Pathogenesis, Epidemiology, And Prevention
Klebsiella Oxytoca is a Gram-negative, opportunistic pathogen that can cause a variety of infections, including pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and bloodstream infections. It is a member of the Enterobacteriaceae family, which also includes other well-known pathogens such as Escherichia coli and Salmonella. Klebsiella Oxytoca is often found in the environment, including in soil, water, and sewage. It can also be found on the skin and in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and animals.

Epidemiology of Klebsiella oxytoca-Associated Diarrhea Detected by - Source journals.asm.org
Klebsiella Oxytoca is transmitted through contact with contaminated food, water, or surfaces. It can also be spread through contact with infected people or animals. The symptoms of Klebsiella Oxytoca infection can vary depending on the type of infection. Pneumonia caused by Klebsiella Oxytoca can cause symptoms such as fever, cough, shortness of breath, and chest pain. Urinary tract infections caused by Klebsiella Oxytoca can cause symptoms such as burning or pain during urination, increased frequency of urination, and urgency to urinate. Bloodstream infections caused by Klebsiella Oxytoca can cause symptoms such as fever, chills, and hypotension.
Klebsiella Oxytoca is a serious pathogen that can cause a variety of infections. It is important to be aware of the risks of Klebsiella Oxytoca infection and to take steps to prevent infection. These steps include washing your hands frequently, avoiding contact with contaminated food and water, and seeking medical attention if you have symptoms of infection.
| Pathogenesis | Epidemiology | Prevention |
|---|---|---|
| Klebsiella Oxytoca produces a variety of virulence factors that allow it to cause infection. These virulence factors include fimbriae, which allow the bacteria to attach to host cells, and toxins, which can damage host cells. | Klebsiella Oxytoca is a common cause of healthcare-associated infections. It is often found in the environment, including in soil, water, and sewage. It can also be found on the skin and in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and animals. | There are a number of things that can be done to prevent Klebsiella Oxytoca infection. These include washing your hands frequently, avoiding contact with contaminated food and water, and seeking medical attention if you have symptoms of infection. |