Best News | This years Best News Treats and Viral Events
Polio: Eradicating A Paralyzing Disease Through Prevention And Vaccination
Polio, a once dreaded paralyzing disease, has been brought to the brink of eradication through the concerted efforts of global health organizations, governments, and communities. The development of effective vaccines and the implementation of comprehensive vaccination programs have played a pivotal role in this remarkable achievement.
Editor's Notes: "Polio: Eradicating A Paralyzing Disease Through Prevention And Vaccination" have published today date". Understanding the history, impact, and strategies behind polio eradication is crucial for public health professionals, policymakers, and individuals who seek to contribute to the global fight against this disease.
After painstaking analysis and extensive research, we have compiled this comprehensive guide to provide an in-depth understanding of polio eradication, its challenges, and the significant progress that has been made. This guide will empower readers with the knowledge and insights necessary to support continued efforts towards a polio-free world.
Key Differences or Key Takeaways:
Main Article Topics:
FAQ
Polio: Eradicating A Paralyzing Disease Through Prevention And Vaccination is a comprehensive guide that provides crucial information on polio, its prevention, and the significance of vaccination. To enhance understanding, this FAQ section addresses common questions and misconceptions surrounding this paralyzing disease.

Polio and Measles Could Surge After Disruption of Vaccine Programs - Source www.nytimes.com
Question 1: What is polio and how is it transmitted?
Polio is a highly infectious viral disease that primarily affects children under the age of five. It is spread through contact with the feces or saliva of an infected person, or ingestion of contaminated food or water. The virus multiplies in the throat and intestinal tract, potentially causing paralysis.
Question 2: What are the symptoms of polio?
Polio can manifest in different ways, ranging from mild flu-like symptoms to severe paralysis. Initial symptoms may include fever, headache, nausea, and vomiting. In severe cases, the virus can affect the nervous system, leading to muscle weakness, paralysis, and even respiratory failure.
Question 3: Is there a cure for polio?
Currently, there is no cure for polio. However, vaccination is an effective preventive measure. The polio vaccine stimulates the immune system to produce antibodies that protect against the virus.
Question 4: Why is vaccination important in eradicating polio?
Vaccination is crucial for eradicating polio because it creates herd immunity. When a significant proportion of the population is vaccinated, the virus has less opportunity to spread. As a result, even unvaccinated individuals are protected by the reduced circulation of the virus.
Question 5: Are there any risks associated with the polio vaccine?
The polio vaccine is generally safe and effective. However, as with any vaccine, there is a very small risk of side effects. The most common side effects are mild and may include fever, redness, and swelling at the injection site.
Question 6: How can we contribute to the eradication of polio?
The eradication of polio requires a collective effort. Vaccination is paramount, ensuring that all eligible individuals receive the recommended doses of the polio vaccine. Additionally, promoting good hygiene practices, such as handwashing and proper sanitation, can help prevent the spread of the virus.
By addressing these frequently asked questions, we aim to dispel misconceptions and emphasize the importance of prevention and vaccination in the fight against polio. This paralyzing disease can be eradicated through collective efforts and sustained commitment to public health initiatives.
Tips
Eradicating polio requires a multifaceted approach. These tips provide guidance on prevention and vaccination to effectively combat this paralyzing disease.
Tip 1: Vaccination
Vaccinate children according to the recommended schedule. Vaccination is the primary method of preventing polio, as it stimulates the immune system to produce antibodies that protect against infection.
Tip 2: Maintain High Vaccination Coverage
Ensure that a high percentage of the population is vaccinated to achieve herd immunity, which reduces the likelihood of outbreaks and protects vulnerable individuals.
Tip 3: Surveillance
Establish a robust surveillance system to monitor for suspected polio cases and promptly investigate and respond to prevent further transmission.
Tip 4: Outbreak Response
Develop and implement comprehensive outbreak response plans to rapidly contain and control outbreaks, including targeted vaccination campaigns and enhanced surveillance.
Tip 5: Sanitation and Hygiene
Promote good sanitation and hygiene practices, such as handwashing and proper waste disposal, to reduce the risk of transmission through contaminated water or food.
Summary
By implementing these tips, healthcare professionals and communities can contribute significantly to the eradication of polio and ensure the protection of future generations from this debilitating disease.
Polio: Eradicating A Paralyzing Disease Through Prevention And Vaccination
Polio, a crippling disease that primarily affects children, has been a global health concern for centuries. Through concerted efforts involving prevention and vaccination programs, we have come far in our fight against polio, and its eradication is within reach.
- Transmission: Polio is spread through contact with the feces of an infected individual.
- Paralysis: The virus can cause irreversible paralysis, often affecting the legs.
- Vaccine: The polio vaccine, available in both oral and injectable forms, is highly effective in preventing the disease.
- Herd Immunity: Vaccination programs aim to achieve herd immunity, where a large proportion of the population is immune.
- Surveillance: Continuous surveillance is crucial for detecting and responding to any outbreaks.
- Eradication: Global initiatives have successfully eradicated polio from most regions.
The key aspects discussed above highlight the significance of prevention and vaccination in eradicating polio. By understanding the transmission, symptoms, and preventive measures, we can empower ourselves to protect children and communities from this debilitating disease. The polio vaccine has proven to be a powerful tool in achieving herd immunity, and as we continue to strengthen surveillance and eradication efforts, we move ever closer to a world free from polio.

Two Strains of Polio Are Gone, but the End of the Disease Is Still Far - Source www.nytimes.com

New Polio Strains That Protect Vaccine Factory Workers - The New York Times - Source nytimes.com
Polio: Eradicating A Paralyzing Disease Through Prevention And Vaccination
Polio is a highly infectious viral disease that can cause paralysis or even death. Prior to the development of a vaccine, polio outbreaks were common worldwide, causing significant morbidity and mortality, particularly among children. The development and widespread use of the polio vaccine have dramatically reduced the incidence of polio, and the disease is now considered to be on the verge of eradication.
The polio vaccine is a safe and effective way to prevent polio. It is given as a series of injections, and it provides long-lasting protection against the disease. The vaccine has been used successfully in mass immunization campaigns in many countries, and it has played a major role in the global effort to eradicate polio.
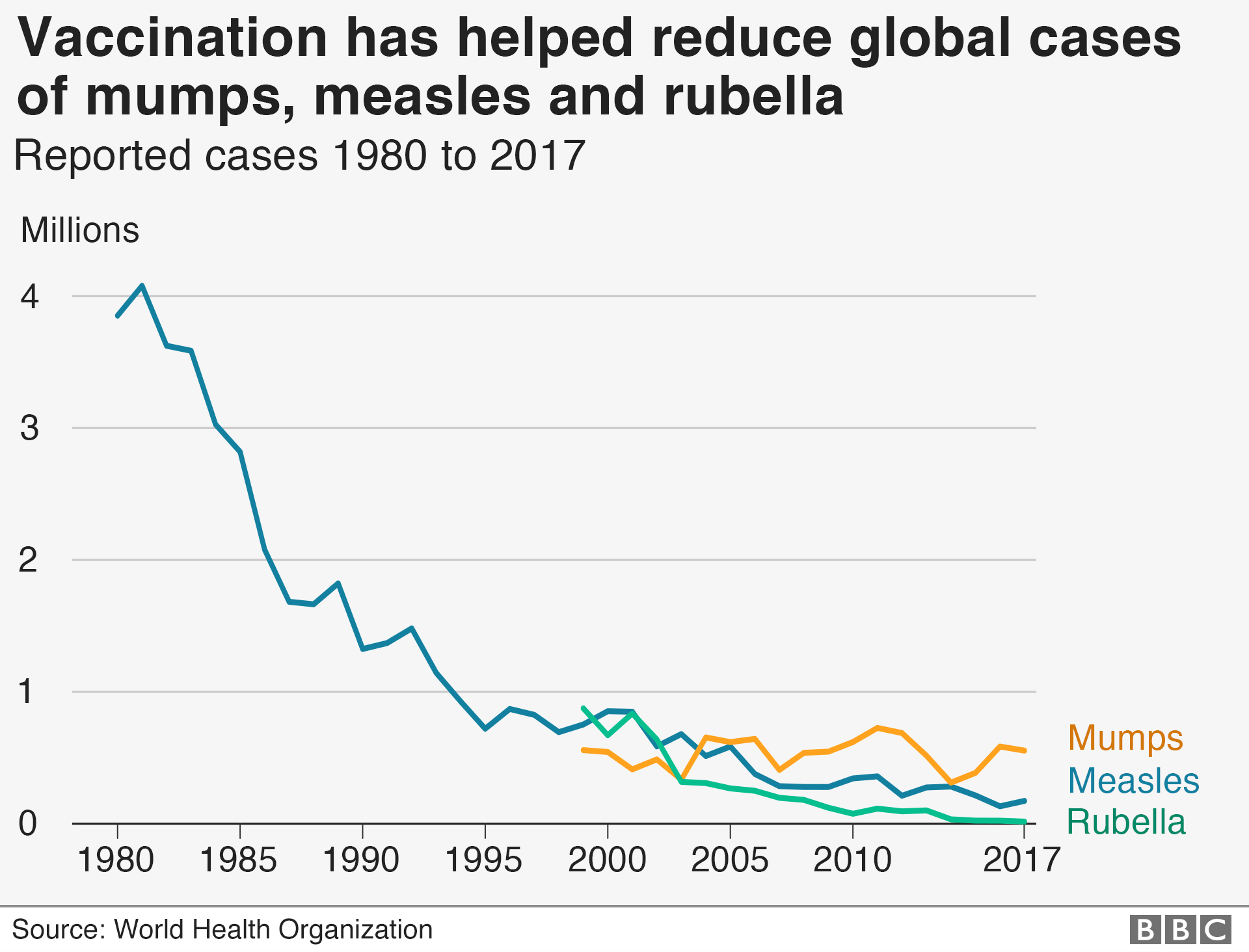
What are vaccines, how do they work and why are people sceptical? - Source www.bbc.com
The eradication of polio is a major public health achievement. It has saved countless lives and prevented countless cases of paralysis. The success of the polio eradication effort is a testament to the power of vaccination and the importance of global cooperation.
However, the eradication of polio is not yet complete. There are still a few countries where polio is endemic, and there is a risk of the disease spreading to other countries. It is important to continue to vaccinate children against polio and to support the global eradication effort.
Table: Key Points on the Connection between "Polio: Eradicating A Paralyzing Disease Through Prevention And Vaccination"
| Cause | Effect |
|---|---|
| Poliovirus infection | Paralysis or death |
| Polio vaccine | Prevention of polio |
| Mass immunization campaigns | Reduction in polio incidence |
| Global cooperation | Eradication of polio |
Conclusion
The eradication of polio is a major public health achievement that has saved countless lives and prevented countless cases of paralysis. The success of the polio eradication effort is a testament to the power of vaccination and the importance of global cooperation.
However, the eradication of polio is not yet complete. There are still a few countries where polio is endemic, and there is a risk of the disease spreading to other countries. It is important to continue to vaccinate children against polio and to support the global eradication effort.